Ultradent Consepsis™ 2% Chlorhexidine Antibacterial Solution Indispense Refill 30ml
Share
Product Information
Endodontic
Consepsis antibacterial solution is recommended for procedural endodontic disinfection, as a final endodontic rinse prior to canal obturation,1,2 and prior to pulp capping. Consepsis solution should be used after smear layer removal for canal disinfection. Sodium hypochlorite and EDTA solutions should be rinsed and removed prior to using Consepsis solution.
Use with NaviTip™ 31 ga - Double Sideport Irrigator tip and NaviTip™ 30 ga/25 mm tip
Note: DO NOT mix Consepsis solution (or any chlorhexidine solution) and ChlorCid™ solution (sodium hypochlorite) in the canal as a harmful brown precipitate will form.
Bonding
Consepsis solution is a 2.0% chlorhexidine gluconate solution free of emollients that interfere with bond strength.
Minimize post-op sensitivity by thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting the preparation prior to restoring. Use prior to cementation, luting (provisional and/or permanent), and direct restorative placement, as well as procedural endodontic disinfection. Disinfect with near-neutral Consepsis solution prior to pulp capping.
- No bond strength compromise
- Syringe delivery makes placement easy
- Reduces potential for postoperative sensitivity
- Use with Blue Mini Dento Infusor tips and Black Mini Brush tips
- Certified gluten free
MDA Registration No: GA6315523-145950

Clinicals
Disinfect Preparations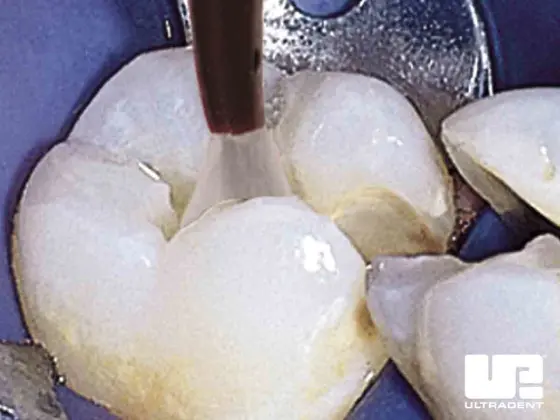
Disinfect preparations by applying Consepsis antibacterial solution with the Blue Mini™ Dento-Infusor™ tip or Black Mini™ Brush tip.
Disinfect Canals
Use Consepsis antibacterial solution to disinfect canals during endodontic procedures, or as an interappointment intraoral medication.
Videos
Research & Studies
In vivo antimicrobial activity of 2% chlorhexidine used as a root canal irrigating solution
Leonardo MR, Filho MT, Silva LAB, Filho PN, Bonifácio KC, Ito IY. In vivo antimicrobial activity of 2% chlorhexidine used as a root canal irrigating solution. J Endod. 1999;25(3):167-71.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10321180 – Leonardo MR, Filho MT, Silva LAB, Filho PN, Bonifácio KC, Ito IY.
Antimicrobial substantivity of root canal irrigants and medicaments: a review.
Mohammadi Z, Abbott PV. Antimicrobial substantivity of root canal irrigants and medicaments: a review. Aust Endod J. 2009;35(3):131-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19961451 – Mohammadi Z, Abbott PV
In vivo preservation of the hybrid layer by chlorhexidine.
Carrilho MRO, Geraldeli S, Tay F, et al. In vivo preservation of the hybrid layer by chlorhexidine. J Dent Res. 2007;86(6):529–533.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17525352 – Carrilho MRO, Geraldeli S, Tay F, et al.
Reviews
Be the first to review
Write an review
How would you rate the product?
More thought about the product


